1. ‘Squirtable’, elastic glue seals wounds in 60 seconds
Biomedical engineers from the University of Sydney and United States worked together to develop a highly elastic, adhesive surgical glue that quickly seals wounds in body tissue.
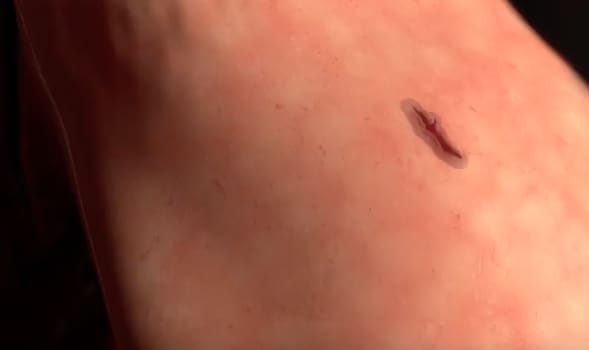
MeTro sets in just 60 seconds after treatment with UV light and even has applications for internal wounds.
Professor from the Charles Perkins Centre said, “When you watch MeTro, you can see it act like a liquid, filling the gaps and conforming to the shape of the wound.”
.
2. How to kill cane toads humanely
Introduced to Queensland in 1935, cane toads are now widespread across north-eastern NSW and considered a threat to biodiversity.

In 2015, Professor from the led research that found a pain-free way for the general public to humanely kill the invasive species.
The research provides a simple solution to a difficult dilemma. The researchers implanted small data-loggers in the brains of cane toads to measure pain responses.
They then put the toads into a refrigerator for a few hours, before transferring them to a household freezer. The toads quietly slipped into unconsciousness as they froze, and their brains did not register any evidence of pain during the process.
from Professor Rick Shine.
3. Students involved in arts see benefits inside and outside classroom
Ever wondered if the arts have an impact on academic and personal wellbeing?
The arts should be central to schooling and not left on the fringes.
A study by the University of Sydney and the Australian Council for the Arts found students who are involved in the arts have higher school motivation, engagement in class, self-esteem and life satisfaction.
Positive effects also resulted from home influences, such as how often parents and their children talked about and participated in the arts.
Co-author of the study, Professor Michael Anderson from the School of Education and Social Work, said, “This study provides new and compelling evidence that the arts should be central to schooling and not left on the fringes.”
about the research.
4. Antidote to deadly box jellyfish sting
Researchers studied the most venomous creature on earth to learn how venom works and what causes pain.
Using CRISPR genome editing, Associate Professor and Dr uncovered a medicine that blocks the symptoms of a box jellyfish sting if administered to the skin within 15 minutes after contact.
The Charles Perkins Centre researchers hope to develop a topical application for humans.
.
5. How coal mines impact on the health of locals
In 2012, a major review of evidence on the impact of coal mining highlighted serious, ongoing health and social problems as well as an urgent need for improvements in government coal mining policy.
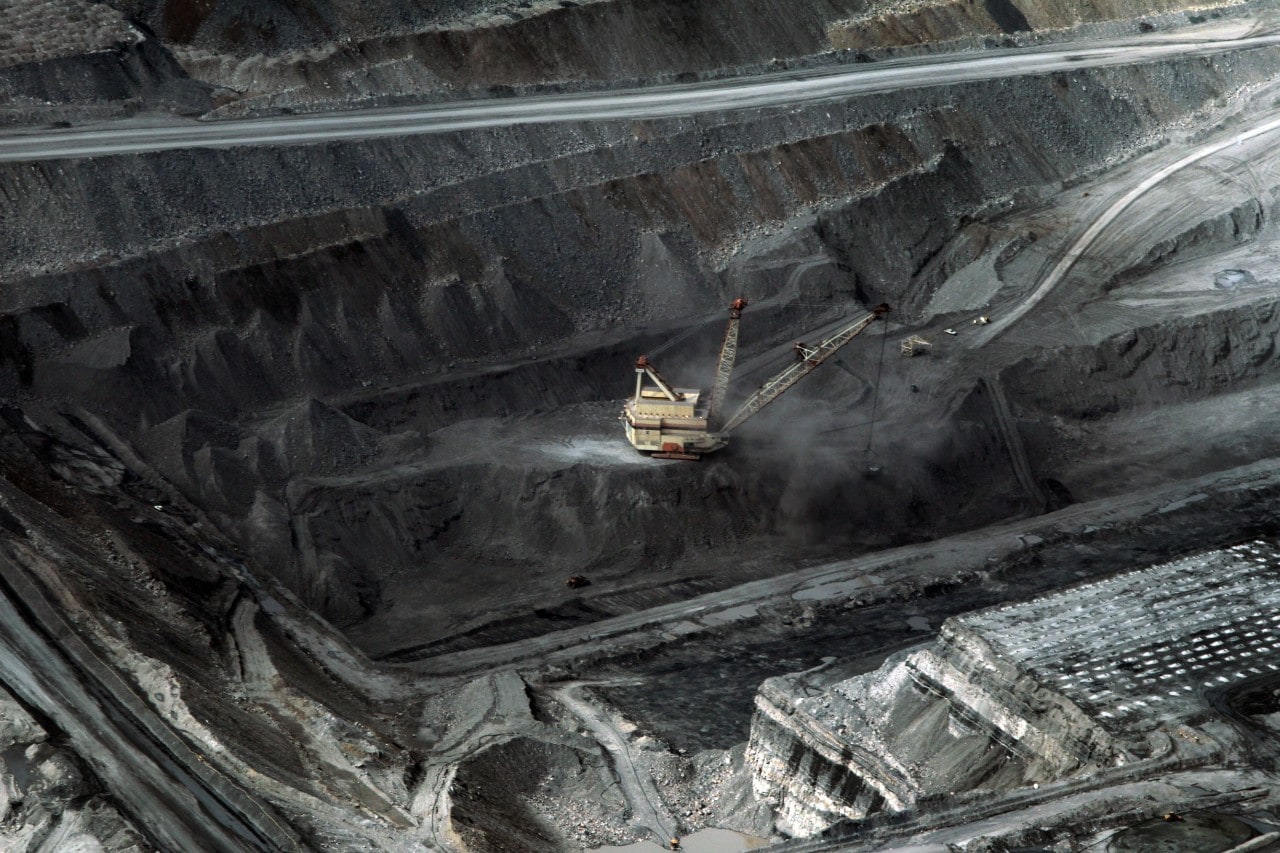

Analysing 50 peer-reviewed research papers from ten countries, the research found a critical lack of local studies investigating the effect of coal mining on Australian communities.
Lead author Associate Professor Ruth Colagiuri said when the report was released, “This comprehensive review of Australian and international health and medical literature underlines the pressing need for Australia to re-evaluate whether the overall health and social costs of Australia’s reliance on a coal economy will ultimately outweigh its economic benefits.”
.
6. Flu shots boosted by exercise
Flu vaccines are considered a great way to lessen your odds of catching the disease and in 2013, University of Sydney researchers advised exercise may be key to a successful vaccination.
Writing in a commentary for the journal , Dr from the Faculty of Health Sciences and Dr from the Faculty of Medicine and Health said exercise both before and after a vaccine could potentially boost the vaccine response.
The researchers added, based on previous studies, physical activity after a shot might not only make the vaccine work better, it might protect them from some side effects as well – but warned not to overdo it and engage in moderate activities such as cycling.
.
7. Whitlam, Medibank and health system reform
Medicare, Australia’s universal health insurance scheme, might enjoy strong support today but at its origins was bitter opposition.
The battle for Medibank was the most bitterly fought political and constitutional struggle of the Whitlam government.
Writing in Making Medicare: The Politics of Universal Health Care in Australia released in 2013, Associate Professor , Deputy Director of the University’s Menzies Centre for Health Policy, and his co-author Anne-Marie Boxall explored the history of the scheme’s introduction.
Describing it as the “most bitterly fought political and constitutional struggle of the Whitlam government,” it went through multiple iterations from its beginning 1974 to its revival in 1984, with the authors writing the Coalition’s opposition to the scheme likely kept them out of office until 1996.
The authors concluded that the scheme was far less radical than it appeared and ultimately offered little critique of how health care was actually delivered.
.
8. People living with dementia lose the ability to daydream
Research by neuroscientists showed people living with frontotemporal dementia – a form of younger-onset dementia – lose the ability to daydream.
While most healthy people daydream approximately 50 percent of their waking lives, people living with frontotemporal dementia became increasingly fixed on their external environment, losing the ability to mind-wander.
Author of the study, Associate Professor from the Brain and Mind Centre and School of Psychology said, “This study helps us to understand the rigidity and behavioural changes that we typically observe in frontotemporal dementia.
“These behaviours can be particularly difficult to manage, as the individual with dementia may appear apathetic and difficult to motivate, particularly in the absence of external stimulation.”
.
9. Common nanoparticles could impact gut microbiota
Earlier this year, a study provided new evidence that nanoparticles present in common food items could have harmful impacts on human health.
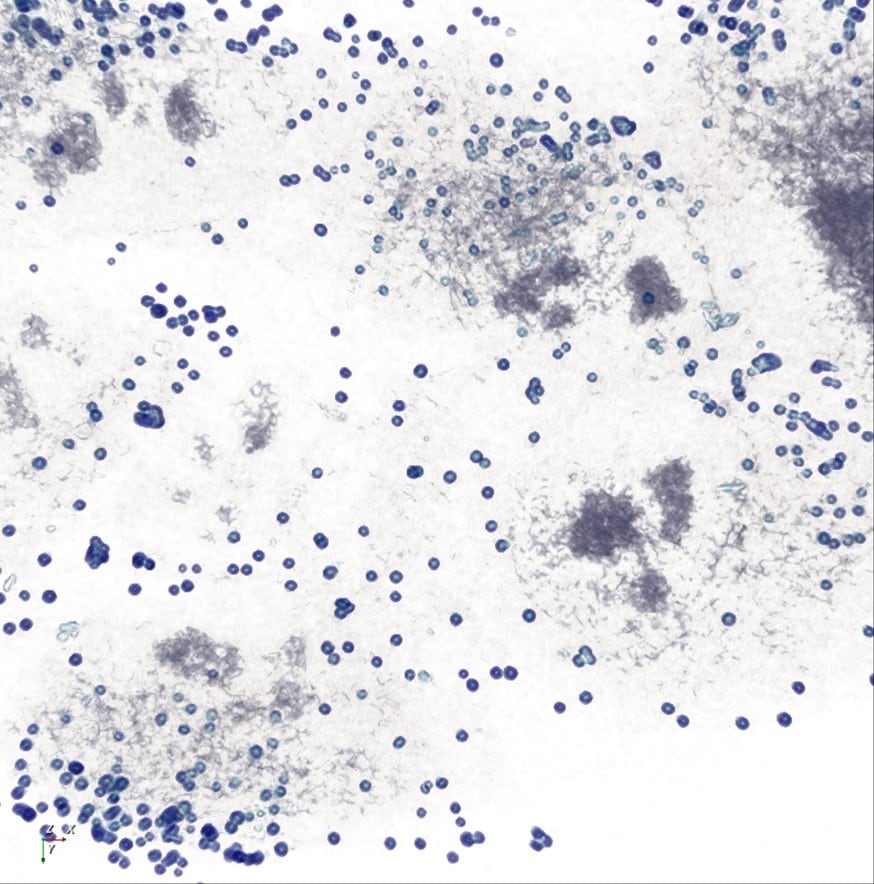
The study investigated the health impacts of food additive E171 (titanium dioxide nanoparticles), which is commonly used food products such as mayonnaise and some medicines as a whitening agent.
The mice study found that consumption of food containing E171 had an impact on the gut microbiota, which could trigger diseases like inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer.
.
10. Protein shakes could have negative side-effects
Amino acids have long been touted by the fitness and bodybuilding communities for their muscle building benefits.
But protein’s popularity has also meant that less attention has been paid to researching its potentially negative side-effects.
Research led by academics from the University of Sydney’s , Professor and Dr , suggests that while delivering muscle-building benefits, excessive consumption of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) may reduce lifespan, negatively impact mood and lead to weight gain.
.








