The , the (Head of Consortium and Academy Director Manabu Ihara, Prof.), and several companies such as Toshiba Corporation and Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corporation are jointly developing a platform “100 kW hydrogen fuel cell – digital twin” for optimizing the design and control of a 100 kw hydrogen fuel cell that seeks to balance carbon neutrality and economic advantage by mixing renewable energy hydrogen/waste plastic hydrogen. They installed the platform in the and started operation of the platform.
Hydrogen generated by renewable energy is expected to contribute to carbon neutrality. However, at the current time, introduction is not progressing as expected due to reasons such as the high cost of water electrolyzer and the incompatibility of electrolyzer sizes. Therefore, in order to increase incentives for introducing hydrogen as a technology for carbon neutrality, this system produces hydrogen by supplying electricity from solar cells in the EEI Building to a small-capacity water electrolyzer. It also mixes an appropriate ratio of hydrogen produced from waste plastic (produced by thermal decomposition of waste plastic, steam reforming, shift reaction, and refining process; Resonac Holdings Corporation) and supplies it to the hydrogen fuel cell. Power from the fuel cell will be supplied to the EEI Building and campus, and waste heat will be supplied to the EEI Building’s air conditioning system (central heating and cooling) for advanced utilization of waste heat.
Aiming for both carbon neutrality and sustainable economic growth, the system is the first in the world to mix renewable energy hydrogen and waste plastic hydrogen, supply the mixture to a fuel cell, and connect it to the building’s air conditioning system for advanced use of electricity and heat. Moving forward, they aim to establish an urban hydrogen energy utilization model that appropriately mixes and optimizes global hydrogen and local hydrogen.
The system is connected to the intelligent energy system ® that performs peak cut control at the Ookayama Campus of Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech). Its detailed real-time operation data is accumulated in a database and used as energy big data for joint research and education between industry and academia. Furthermore, the mixing ratio of renewable energy hydrogen and waste plastic hydrogen to be supplied to the fuel cell can be controlled in real time from Ene-Swallow®. In the future, the acquisition of detailed data will make it possible to design and control the device capacity of the system. As a carbon neutral digital twin (Ene-Swallow® Digital Twin), a platform that can be integrated and linked with the aim of achieving carbon neutral and sustainable economic growth, they will work for further advancement and promotion as part of R&D for “Carbon-neutral digital twin with the core of energy bigdata” in the JST-MIRAI Program “Advanced Intelligent Information Society” mission area (Program Officer: Eisaku Maeda).
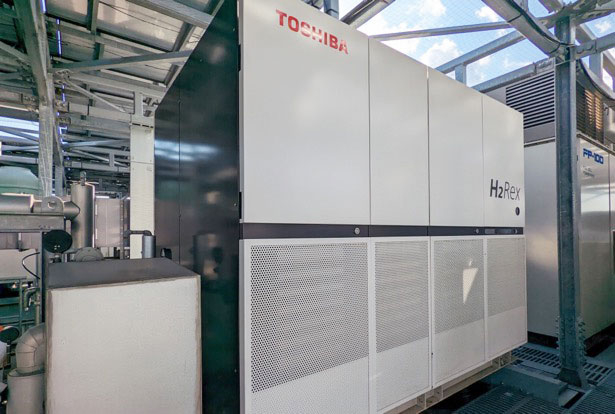

Hydrogen fuel cell (Toshiba H2RexTM)
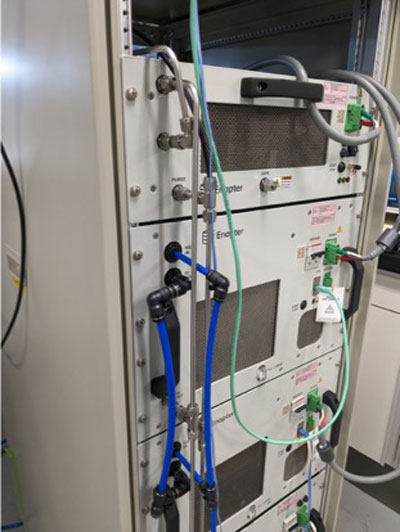

Water electrolyzer
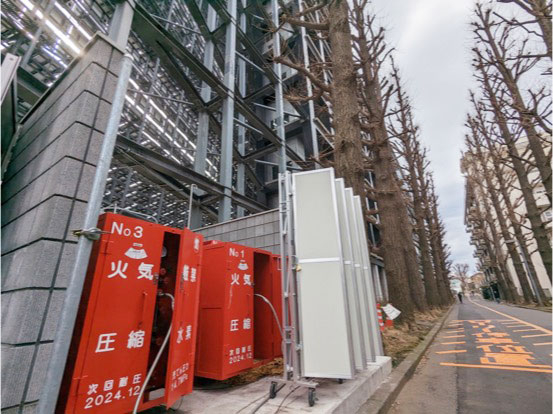

Storage racks for hydrogen generated from waste plastics
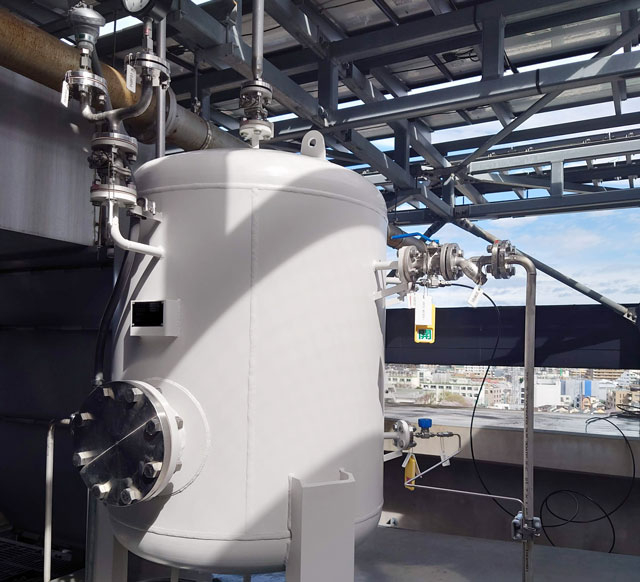

Reservoir for mixing renewable energy hydrogen and waste plastic hydrogen
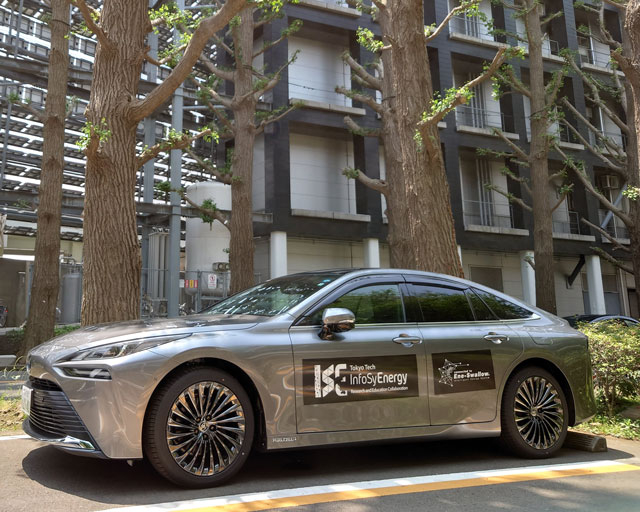
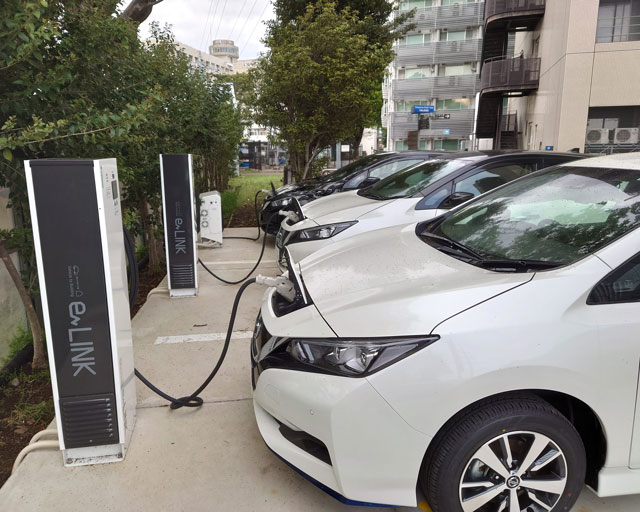


A fuel cell vehicle(left) and electric vehicles(right) connected to Ene-swallow®
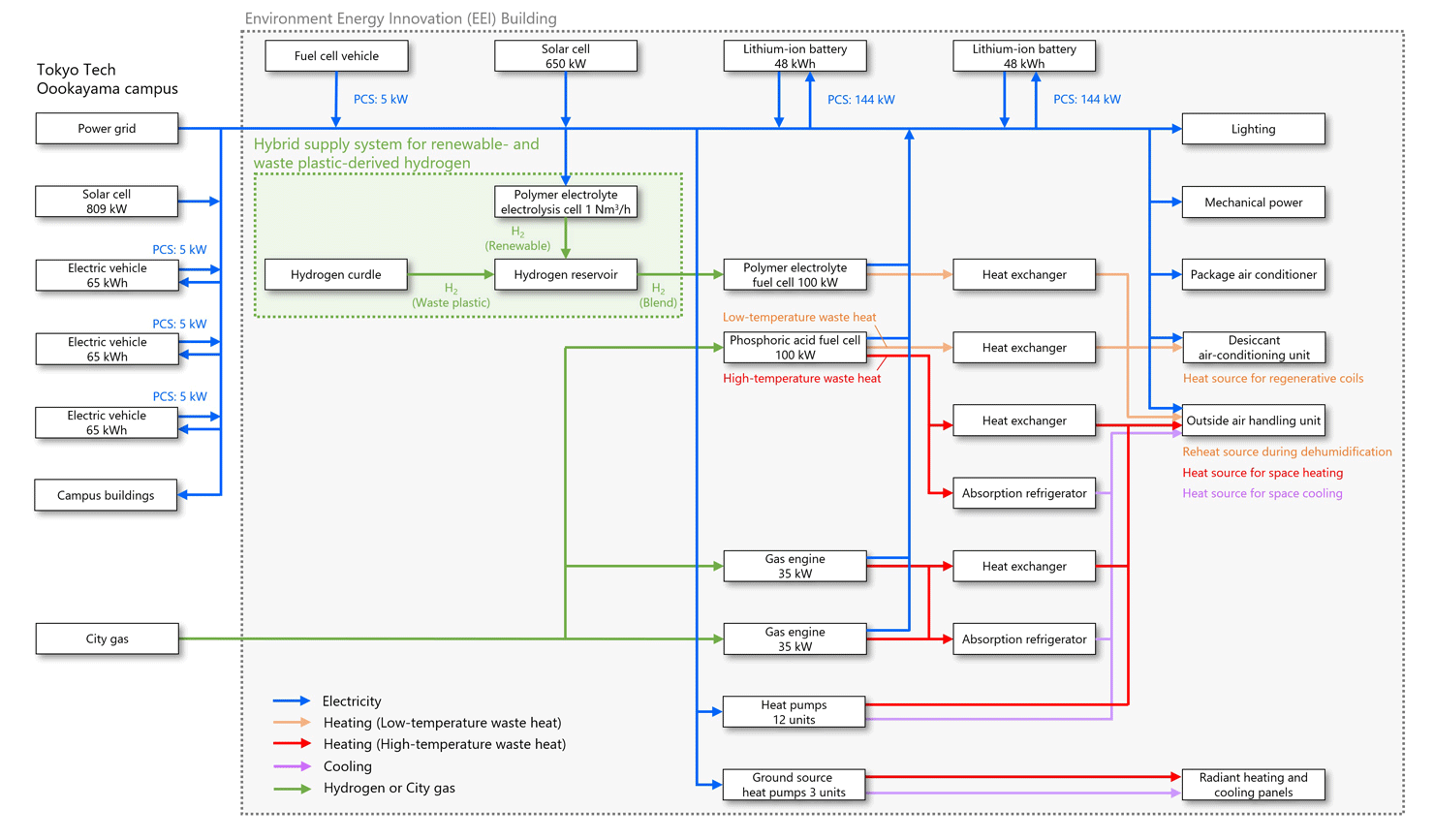
Overview of exhaust heat utilization in 100 kW hydrogen fuel cell system that supplies a mixture of renewable energy hydrogen and waste plastic hydrogen / Overview of connected energy devices
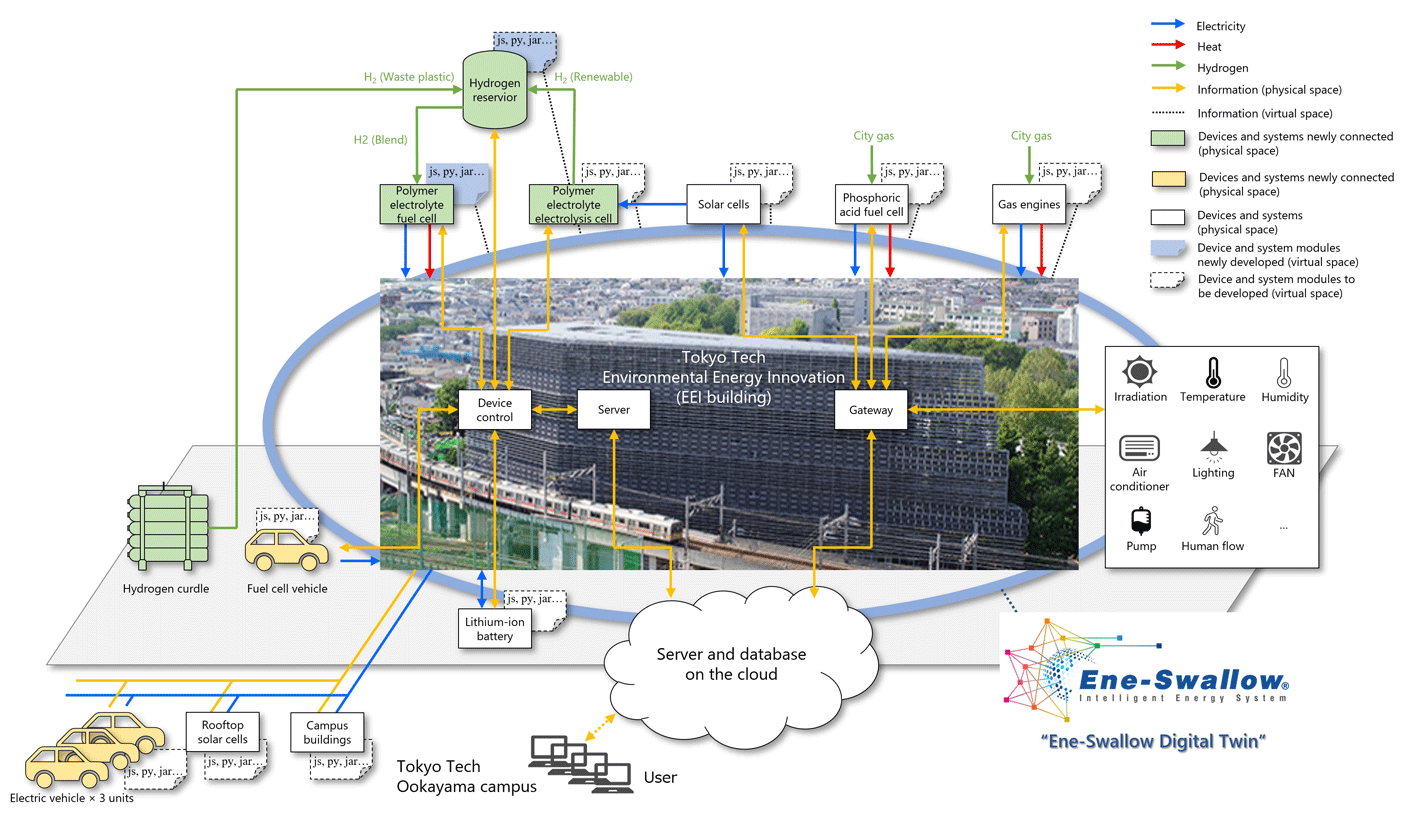
Overview of Ene-Swallow® Digital Twin
Joint Developers of the System
Conceptual design, Information system design/implementation (fuel cell, electrolysis cell and information system) and Design supervision
- Tokyo Tech Academy of Energy and Informatics
- InfoSyEnergy Research and Education Consortium, Tokyo Institute of Technology
- Ihara-Manzhos laboratory (Department of Chemical Science and Engineering, School of Materials and Chemical Technology, Tokyo Institute of Technology)
Hydrogen fuel cell – Manufacturing, Implementation and Data acquisition
- Toshiba corporation
- Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corporation
Support for information system implementation
- NTT Data Business Systems Corporation
- NTT Data Customer Service Corporation
Hydrogen fuel cell system – Design and implementation of hydrogen supply device
- UEKI Corporation
- Resonac Holdings Corporation
Hydrogen fuel cell system – Design and implementation for waste heat utilization in EEI building
- NIHON SEKKEI, INC.
- Azbil Corporation
Electrical, mechanical and architecture – Facilities Implementation
Tokyo Tech, Facilities Construction and Maintenance Division, Facilities Department






