Metal-air batteries have been pursued as a successor to lithium-ion batteries due to their exceptional gravimetric energy densities. They could potentially enable electric cars to travel a thousand miles or more on a single charge.
A promising new member of the alkali-metal-air battery family is the potassium-air battery, which has more than three times the theoretical gravimetric energy density of lithium ion batteries. A key challenge in designing potassium-air batteries is choosing the right electrolyte, the liquid which facilitates the transfer of ions between the cathode and anode.

Typically, electrolytes are chosen using a trial-and-error approach based on rules of thumb correlating several electrolyte properties, followed by exhaustive (and time consuming) testing of several electrolyte candidates to see if the desired performance is achieved.
Researchers from Washington University in St. Louis, led by Vijay Ramani, the Roma B. and Raymond H. Wittcoff Distinguished Professor of Environment & Energy at the McKelvey School of Engineering, have now shown how electrolytes for alkali-metal air batteries can be chosen using a single, easy-to-measure parameter.
Their work was published July 8 in the .
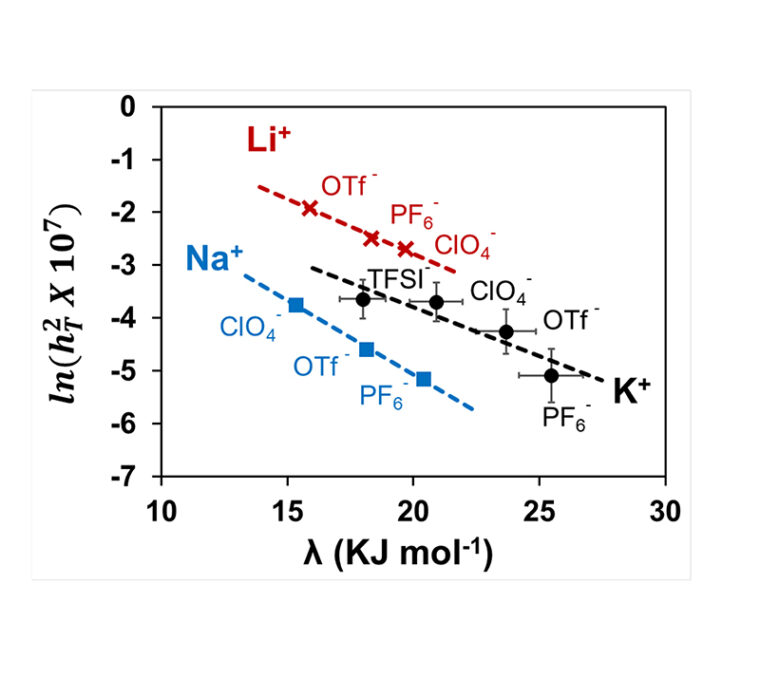
Ramani’s team studied the fundamental interactions between the salt and solvent in the electrolyte and show how these interactions can influence overall battery performance. They developed a novel parameter, namely the “Electrochemical” Thiele Modulus, a measure of the ease of ion transport to and reaction at an electrode surface.
Showing how a single parameter descriptor of the solvation energy correlates with both ion transport and surface reaction kinetics is a breakthrough advance. It will allow us to rationally develop new high-performance electrolytes for metal-air batteries.
Vijay Ramani
This research documents the first time that the Nobel Prize-winning Marcus-Hush theory of electron transfer has been used to study the impact of electrolyte composition on the movement of ions through the electrolyte, and their reaction at the surface of the electrode.
This Thiele Modulus was shown to exponentially decrease with increasing solvent reorganization energy – a measure of the energy needed to modify the solvation sphere of a dissolved species. Thus, the solvent reorganization energy could be used to rationally select electrolytes for high performance metal-air batteries. No more trial-and-error.
“We started out trying to better understand the influence of the electrolyte on the oxygen reduction reaction in metal-air battery systems,” said Shrihari Sankarasubramanian, a research scientist on Ramani’s team and lead author of the study. “We ended up showing how the diffusion of ions in the electrolyte and the reaction of these ions on the electrode surface are both correlated to the energy needed to break the solvation shell around the dissolved ions.”
“Showing how a single parameter descriptor of the solvation energy correlates with both ion transport and surface reaction kinetics is a breakthrough advance,” Ramani said. “It will allow us to rationally develop new high-performance electrolytes for metal-air batteries.”
Joshua Kahky, a rising junior in the Department of Energy, Environmental and Chemical Engineering, is second author of the study. He helped carry out the study as an undergraduate summer intern in Ramani’s lab.




